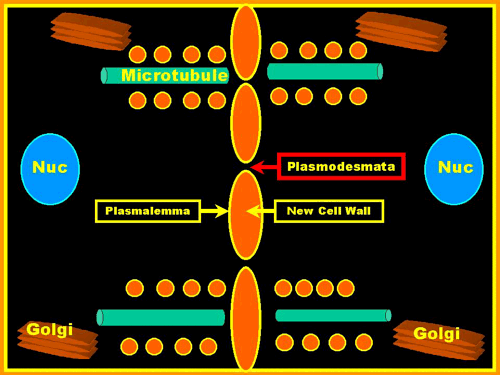
Microtubules appear to guide the movement of the Vesicles & these become more
peripheral as the new wall grows.There are gaps in the Cell Plate. These become
Plasmodesmata and connect the cytoplasm of both new cells. This process progresses from
the center towards the to the periphery until the New Wall joins the Old Wall.
|