 |
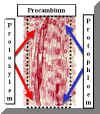
Phloem also comes from the Procambium. Protophloem differentiates from the outermost Procambium, directly opposite the Xylem. Phloem differentiation is hard to follow because the Sieve Elements do not have dramatic features like the Tracheary Elements in Xylem. | |
|
Xylem is clearly visible in the attached illustration. It is harder to specifically identify the Phloem. However, careful inspection leads to the conclusion that the tissue immediately opposite the xylem arose from the same shaft of cells (Procambium) as the xylem. Consequently, we can be fairly confident that the nonlignified cells with small diameters, adjacent to the xylem in this vascular bundle are the Phloem. | |
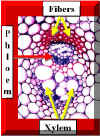 |
Many plants produce Vascular Bundles which contain a "cap" of Fibers. These are usually associated with the Phloem. Thus, the Phloem can be located between the Fibers and the Xylem. Furthermore, Phloem cells may have a characteristic organizational pattern based on cell sizes which helps to locate it. | |
 Sugarcane Vascular Bundle stained with Toluidine Blue |
In many monocots like Sugarcane the Phloem is highly organized and has a regular pattern of narrow and wide cells. The wide cells are the Sieve Tube Members. The small cells are Companion Cells. Fibers surround the vascular bundle in this case. | |
 Phloem of a Sugarcane Vascular Bundle stained with Toluidine Blue |
Companion Cells (CC) and Sieve Tube Members (STM) develop from the same progenitor cell. The STM are analogous to Vessel Members. They are columnar cells which unite vertically to form a Sieve Tube. STM are enucleate at maturity and depend on the Companion Cells to regulate their physiological processes. Each STM has one to several CCc. The pink color in one of the STM is due to the presence of a Sieve Plate which is analogous to the Perforation Plate of Vessel Members. | |
 |
Locate the various cells in this
unlabeled image of a Sugarcane Vascular Bundle stained with Toluidine
Blue. CC=Companion Cells, F=Fibers, STM=Sieve tube member, VM=Vessel Member |
|
 Sieve Plates from the image above. |
Sieve Plates occur on endwalls. of STM. They contain large Sieve Pores. These are much larger than Plasmodesmata. The Plasmalemma and Cytoplasm are continuous from one STM to another through the Sieve Pores. | |
| Home Page | ||
|---|---|---|

