 |
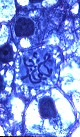
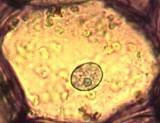
A "typical" Parenchyma Cell is Isodiametric, has thin walls, a large central Vacuole & well developed Plastids. | |
| Parenchyma cells can begin differentiating close to meristematic cells. Parenchyma cells are not mitotic but can become so following injury . | ||
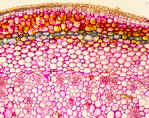 |
Parenchyma cell walls generally contain large quantities of Pectins & stain pink with Toluidine Blue. | |
 |
Parenchyma Tissues are usually massive and contain many adjacent Parenchyma cells. This image is from a stem, stained with Toluidine Blue | |
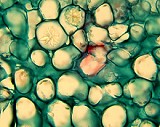 |
Commercial slides are typically stained with Fast Green and Safranin. Parenchyma cells may appear green with these stains. The green material between cells is probably a carbohydrate secreted by the adjacent parenchyma cells. Find the crystals in this image. | |
Prior Page |
Home Page | Next Page |