Mineral Nuitrients
Nutrients Needed
Essential:
- cannot complete life cycle without it or
- forms part of essential molecule
Macronutrients: >1000 ppm needed
| C | H | O | P | K | N | S | Ca | Fe | Mg
|
|---|
| air & water | limited in soil | usually common in soil
|
|---|
| P |
nucleic acid, phospholipid, reproduction
|
|---|
| K | ion balance, enzymes
|
|---|
| N | protein, nucleic acid, etc.
|
|---|
| S | cysteine, methionine, CoA, etc.
|
|---|
| Ca | enzyme cofactor, cyclosis
|
|---|
| Fe | cytochromes, other enzymes
|
|---|
| Mg | chlorophyll, enzyme cofactor
|
|---|
CaMg found in lime
Fe and S common in minerals
Macronutrients: <100 ppm needed
Co Mn Cu Zn B Mo Si Al Cl etc.
amount needed found in soil
| Co | enzyme cofactor
|
|---|
| Mn | enzyme cofactor
|
|---|
| Cu | enzymes, plastocyanin, cytochrome oxidase
|
|---|
| Zn | enzyme cofactor
|
|---|
| B | pollen tube growth and orientation?
|
|---|
| Mo | nitrate reductase cofactor
|
|---|
| Si | cell wall component
|
|---|
| Al | enzyme cofactor
|
|---|
| Cl | ion balance, stomatal function
|
|---|
Fertilizer: Nitrogen - Phosphorus - Potassium (NPK analysis)
balance important:
20-20-20 a common general purpose fertilizer
10-20-10 common flower or fruit garden ("vegetables")
(phosphate needed for reproduction)
40-0-0 urea or ammonium nitrate for lawn and true vegetables
(only nitrogen needed for reasonable leaf stem growth)
(economical)
0-40-0 super phosphate
0-0-30 potash
make your own mixture for exact needs
BASED ON SOIL TEST!
Avoid pollution caused by over-use of fertilizer (eutrophication)
Nutrients available only through WATER in the soil:
Water Dissociates:
H2O ------> OH- + H+ 10-7 M = distilled water
pH = - log [H+] = 7 for distilled water pouvoir HydrogŹne
pH Scale 0 to 14:
| H+ Conc: | 100 | 10-7 | 10-14 M
|
|---|
| pH | 0 | 7 | 14
|
|---|
| description: | acid | neutral | base
alkalai
|
|---|
| taste: | sour | sweet | bitter
|
|---|
| example: | vinegar | dH2O | soap
|
|---|
| Optimal for plants: | cranberries | common
garden | grass
beans
asparagus
|
|---|
HOW TO ADJUST pH:
lime = Ca(OH)2 ----------->
Al + H2SO4 <------------- Al2(SO4)3 aluminum sulfate + H2O
How Acid affects nutrients available:
Clay Particle has negative charge

Opposites attract so metal ions with positive charge stick:

Acid rain = H+ This smaller ion replaces large metal ions
= (cation exchange)
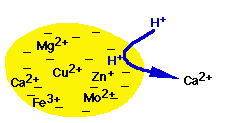
Released Cations available for uptake into roots or leach out!
Roots secrete acid, retrieve ions, retrieve acid ions.
Can you Overdose the Nutrients?

Deficiency Symptoms
Stunted Growth (all, esp N (stem) and P (root))
Chlorosis (decreased chlorophyll synthesis, increased degradation, Mg N Fe
Necrosis (Mg K Mn)
Color Change (P)
Mobile = deficiency symptom in older leaf (N P Mg Cl)
Intermediate = deficiency throughout (K Zn Cu Mn S)
Immobile deficiency symptoms in younger leaf (Ca B Fe)
Precipitation Deficiency:
| 2 Fe3+ + 6 OH- | alkaline pH
------------->
western soil | 2 FeOH3 --> Fe2O3. 3H2O = insoluble rust |
|---|
Similar effect with Zn, Mn, Cu, Ca, etc.
Chelating Agents (ligands):
electrons from -COOH or -NH4+ prevent oxidation
EDTA: Ac2N-CH2-CH2-NAc2 ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid = Versene
EDDHA: ethylene diamine di (o-hydroxyphenyl) acetic acid = Sequestrene
Natucral chelating agents:
- Catechols from bacteria
- Hydroxamates (peptides) from fungi
- Citrate from plants
Hydroponics: Hoagland's solution 1938
Go back to the Course Schedule.



