1961-F. T. Addicott et al. University of California, Davis
Studying substances that accelerate leaf abscission
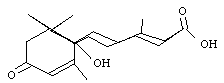
1961-Liu and Carns isolate "abscisin" crystals from cotton petioles
1963-Ohkuma et al isolate "abscisin II" from young cotton fruit C15H20O4
1963-C. F. Eagles and P. F. Wareing isolate "dormin" from Betula pubescens
Causes buds of growing seedlings to go dormant
1965-Wareing and others compare "dormin" and "abscisin II"...identical
1967-Closed-door session between Adicott's group and Wareing's group
Abscisic acid is the "acceptable compromise" name...ABA is abbreviation
Since then it is known to be involved mostly in dormancy NOT abscission?
Found in all higher plants, ferns, mosses (1 nM to 1 uM pool size)
Lunularic acid found in liverworts and algae (structural analog)
Not found in fungi and bacteria

Increases rapidly in water-stressed leaves, causes stomatal closure, synthesis decreases as water potential increases back to normal.
Increases rapidly in water-stressed leaves, but is outstripped by synthesis until the recovery phase.
Stomatal closure--protection from water stress!
Guard cells "leaky", lose K+, lose turgor, close (less than 3 minutes!)
Increases during "lag" phase before stomatal closure (t-10 min)Bud dormancy
Long nights, increased AbA, decreased growth, buds dormant
(potato tubers, ash and birch buds)
NOTE: temperate zone plants adapted to daylength changes...NOT tropicals!
Temperate zone adaptation considered ADVANCED
Reversible with GA! Dormancy break!Seed dormancy
Degraded during stratification...growth in vernalization!
Fraxinus projects with F. americana (dormant) and F. ornus (non-dormant)
Degradation of endogenous hormone to levels in non-dormant species!
Exogenous AbA makes both dormant
Reversible with GA (but cytokinin helps restore normal chlorophyll)Abscission?
Unclear...reversed by IAA...maybe involves ethylene...maybe not!
May be limited to cotton and a few other species
Ethylene more universal?...more terminal?
ABA stimulates ethylene biosynthesis?
Further protection of plant from desiccationInhibits amylase synthesis in Barley
Works at the transcription process to decrease mRNA synthesis for amylase
ABA also stimulates several proteins (21, 35, 27, 29 kD) which interfere with amylaseSeed maturation
Viviparous mutants defective in AbA synthesis and/or sensitivity
Some are "wilty" mutants!
Then desiccation occurs to finish the maturation process
Go back to the Course Schedule.