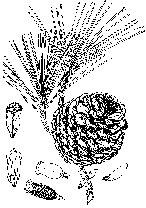
"Pinus taiwanensis Hayata" (2).
Common Names
Luchu pine; Ryukyu Island pine (4).Taxonomic notes
Two subspecies: luchuensis and taiwanensis (Hayata) Li 1997 (syn: P. taiwanensis Hayata 1911) (5). Li (2) describes P. taiwanensis as synonymous with P. brevispica Hayata 1913 and P. luchuensis sensu Wu 1956, non Mayr 1894. P. hwangshanensis has also been described as a subspecies of P. luchuensis.Pinus luchuensis and P. taiwanensis were described from the Ryukyu Islands and Taiwan respectively. There has been no consensus on their inter-relationships for a considerable time (2).
Description
For the type variety: "A large evergreen tree. Leaves two in a fascicle, 8-15 cm. long, dark green, semicircular in cross section, with 2 vascular bundles and 2-3 medial resin ducts. Matured cones ovoid, 4-5 cm. long; scales armed. Seeds winged; wings lanceolate, about double in length as seeds. Trunk bark grayish brown, deeply fissured, furrows about 1.0 cm. in depth, 1.5-4.0 cm. across; ridges flattened, broken into flaky plates; lenticels inconspicuous; outer barks about 0.2-1.5 cm. thick, hard and brittle, more or less ligneous, with a brown cross section; newly formed periderm milky white; inner barks 2-5 mm. thick, pale yellowish white, finely fibrous, gumming pale yellowish, transparent resin after cutting; cambium and newly formed phloem colorless,somewhat transparent, rather thick. Freshly cut sapwood pale apricot yellow, wood rays inconspicuous" (4).For var. taiwanensis: "A large tree, up to 35 m in height and 80 cm in diameter, the trunk straight, the branches horizontal, the bark fissured into small scales. Leaves 2 in a fascicle, semicircular in cross section, more or less rigid, 8-11 cm long, the margins serrulate, generally with 4 resin ducts. Mature cones oblong-ovoid, 6-7 cm long. Seeds winged, 15-18 mm long including the wing" (2).
Liu (4) notes that in comparison with P. luchuensis, P. taiwanensis has dark blue leaves with 4-7 (as opposed to 2-3) resin ducts. Its cones are 6-7 (as opposed to 4-5) cm long. The outer bark is thicker, up to 2.5 cm thick, and in cross section contains tangentially tiered grayish white streaks. The inner bark is pale reddish white (as opposed to pale yellowish white).
The following table, adapted from Li (2) summarizes differences between the three subspecies:
Table 1. Comparison of the subspecies of Pinus luchuensis.
| subsp. luchuensis | subsp. taiwanensis | |
| Length of needles | 12-16 cm | 8-11(-15) cm |
| No. of resin canals | 2-3 | 6-7 |
| Maximum height | 20 m | 35 m |
| Distribution | Ryukyu Is. | Taiwan |
| Altitude | 0-850 m | 750-2500 m |
Range
Taiwan: Chiayi, Xinchu, Ilan, Nantou, & Taichung Xians; Japan: Okinawa, Ryukyu Island; near sea level in Japan, increasing to 750-3500 m in central ranges of Taiwan; in habitats ranging from large pure stands to broadleaf-conifer forest to subalpine meadow (2, 3, 4).Big Tree
Oldest
Dendrochronology
Ethnobotany
Observations
Not seen. Some specific location data (3) follow:Okinawa: 128° 15'50"E, 26°52'17"N, 100 m. Margin of forest. A tree ca. 6-7 m tall.
Taiwan: 121°12'16"E, 24°28'08"N, 2650 m; 120°58'E, 23°35'N; 121°16'E, 24°03'N, 2360-3500 m; otherwise 2150-3450 m. Habitats include primary forest, mixed with Pinus armandii; mixed Tsuga, Chamaecyparis, Pinus and Fagaceae forest on mountain ridge; mixed broadleaf woodland and Pinus plantation; mixed broadleaf-confer forest; and scattered in alpine meadow. Cited trees ca. 4-10 m tall.
Remarks
Citations
(1) Silba 1986.(2) Li 1975.
(3) Botanical Inventory Of Taiwan.
(4) Liu 1970.
[Pinus] [Pinaceae] [home]
This page is from the Gymnosperm Database
URL: http://www.geocities.com/~earlecj/pi/pin/luchuensis.htm
Edited by Christopher J. Earle
E-mail:earlecj@earthlink.com
Last modified on 25-Apr-1999